Quintessenz Zahnmedizin, 7/2018
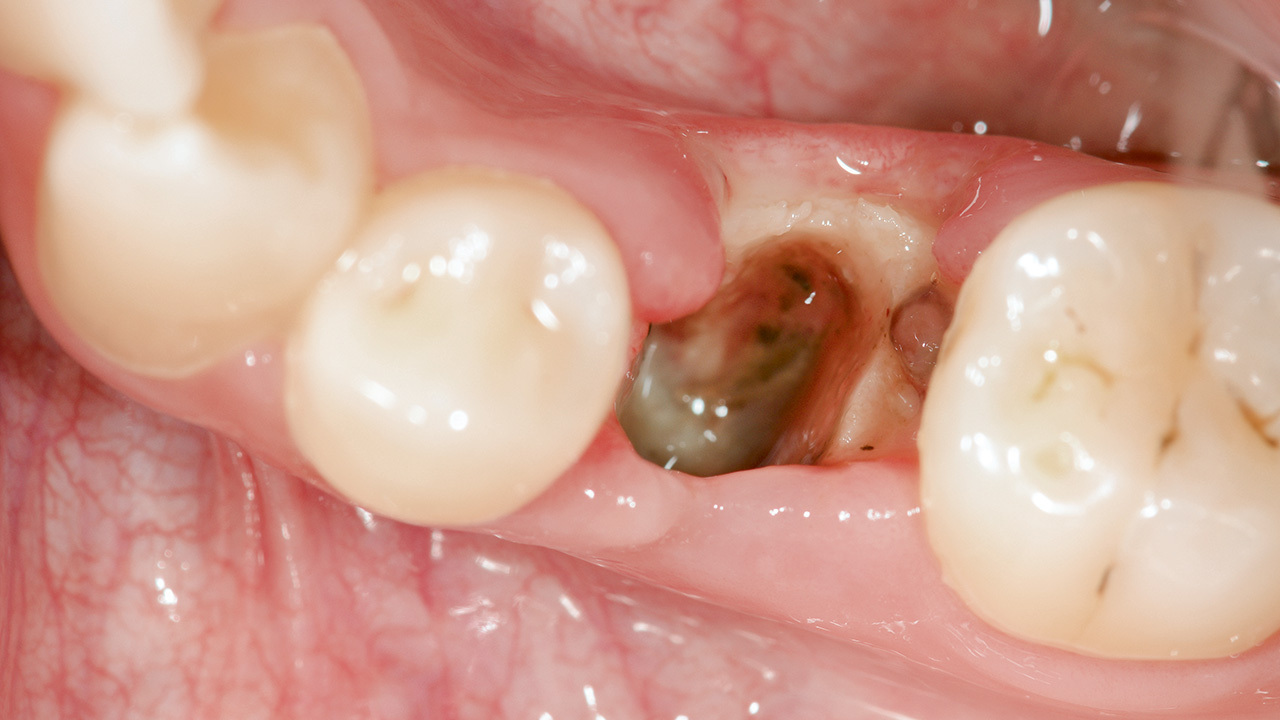
OralchirurgiePages 788-796, Language: GermanBosch, Gabriel / Steinmeier, Sabrina / Stadlinger, Bernd / Rücker, Martin / Giacomelli-Hiestand, BarbaraIm Rahmen oralchirurgischer Eingriffe kann es zu Komplikationen kommen. Häufig beschriebene Komplikationen sind Infektionen im Sinne von Abszessen, Alveolitiden, Osteomyelitiden oder Sinusitiden. In dieser retrospektiven Studie wurde erhoben, wie viele Patienten sich im Jahr 2016 in der Ambulanz der Klinik für Mund-, Kiefer- und Gesichtschirurgie - Klinik für Oralchirurgie der Universität Zürich aufgrund einer postoperativen Infektion nach einem oralchirurgischen Eingriff vorstellten. In diesem Zusammenhang galt das Hauptinteresse der Korrelation zwischen dem Auftreten einer Infektion und der prä- bzw. postoperativen Antibiotikagabe. Im Weiteren wurden der Zeitraum des Auftretens, die Art der Komplikation, die Heilungszeit und verschiedene Einflussfaktoren untersucht. Das Ziel bestand darin, Risikofaktoren zu definieren, die zu einem vermehrten Auftreten von postoperativen Infekten führen können. Zusätzlich wurde der Effekt diverser Einflussfaktoren auf den Heilungsverlauf der Infektion betrachtet.
Keywords: Infektionen, oralchirurgische Eingriffe, Komplikationen, Antibiotika, Abszess, Alveolitis sicca
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, 4/2017
PubMed ID (PMID): 29292410Pages 343-361, Language: English, GermanMehl, Albert / Bosch, Gabriel / Fischer, Carolin / Ender, AndreasStatement of problem: Three-dimensional (3D) intraoral scanning systems allow for the simultaneous acquisition of 3D information about tooth surfaces and a photorealistic view of the patient's tooth colors.
Aim: The goal of this study was the in vivo comparison of a new 3D scanner with a color acquisition mode and conventional visual and digital color measurements.
Materials and methods: The colors of 40 teeth of 20 patients were evaluated in seven ways: 1) By dentists using the Vita 3D-Master; 2) By dental technicians using the Vita 3D-Master; 3) With the 3Shape Trios device; 4) With the Vita Easyshade device; 5) With the Vita Easyshade Advance device; 6) With the SpectroShade device; and 7) With the SpectroShade Micro device. Digital measurements of Groups 3 to 7 were repeated three times for each tooth. For all groups, both the CIE Lab values and the Vita 3D-Master values were recorded. The repeatability and relative accuracy of the Vita 3D-Master values were analyzed statistically using Pearson's chi-squared test (α 0.05). ΔE values were calculated from the CIE Lab values, which served as a basis for performing multidimensional scaling (MDS) and evaluating differences between the groups using the one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tamhane's test (α 0.05).
Results: The results of the ΔE values showed that clinically relevant differences between the evaluation by dentists, dental technicians, and the intraoral scanning device (3Shape) are negligible. The intraoral 3D scanning device (Group 3) and the digital systems (Groups 4 to 7) did not differ significantly in the repeatability of color shade management. The SpectroShade Micro (Group 7) had significantly better relative accuracy than the other devices.
Conclusions: The results demonstrate that intraoral scanning systems can be used to measure both tooth color and tooth surface in 3D.
Clinical implications: Intraoral optical scanning devices allow for the acquisition of accurate 3D surface data. Tooth color can be evaluated simultaneously and can be used to determine the color of restorations without requiring additional conventional color-measurement methods.
Keywords: intraoral scanning, tooth color measurement, spectrophotometer, shade guide, CAD/CAM
Quintessenz Zahnmedizin, 9/2015
ZahnerhaltungPages 1055-1069, Language: GermanAttin, Thomas / Bosch, Gabriel / Wegehaupt, Florian J. / Mehl, Albert / Wiegand, Annette / Blunck, UweDer Übersichtsbeitrag stellt den Einsatz direkter und indirekter Kompositrestaurationen zur Rekonstruktion erosiv stark veränderter Gebisssituationen dar. Es wird zudem eine Einschätzung der für diese Indikation zur Verfügung stehenden Kompositmaterialien vermittelt.
Keywords: Komposit, Erosion, Zahnhartsubstanzverlust, Adhäsivtechnik, CAD/CAM, Bisshebung
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, 3/2015
Open AccessPubMed ID (PMID): 26389137Pages 273-286, Language: English, GermanBosch, Gabriel / Ender, Andreas / Mehl, AlbertAbrasion and erosion are two increasingly common indications for dental treatment. Thanks to modern digital technologies and new restorative materials, there are novel therapeutic approaches to restoring such losses of tooth structure in a virtually non-invasive manner. The case study in this article demonstrates one such innovative approach. The patient's severely abraded natural dentition was restored in a defect-driven, minimally invasive manner using high-performance composite materials in the posterior region, and the "sandwich technique" in the anterior region. The restorations were milled on an optimized milling machine with milling cycles adapted for the fabrication of precision-fit restorations with thin edges.
Keywords: bite raising, CAD/CAM, complex rehabilitation, high-performance composite, non-invasive, ultra-thin occlusal veneers, virtual articulation