International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 2/2025
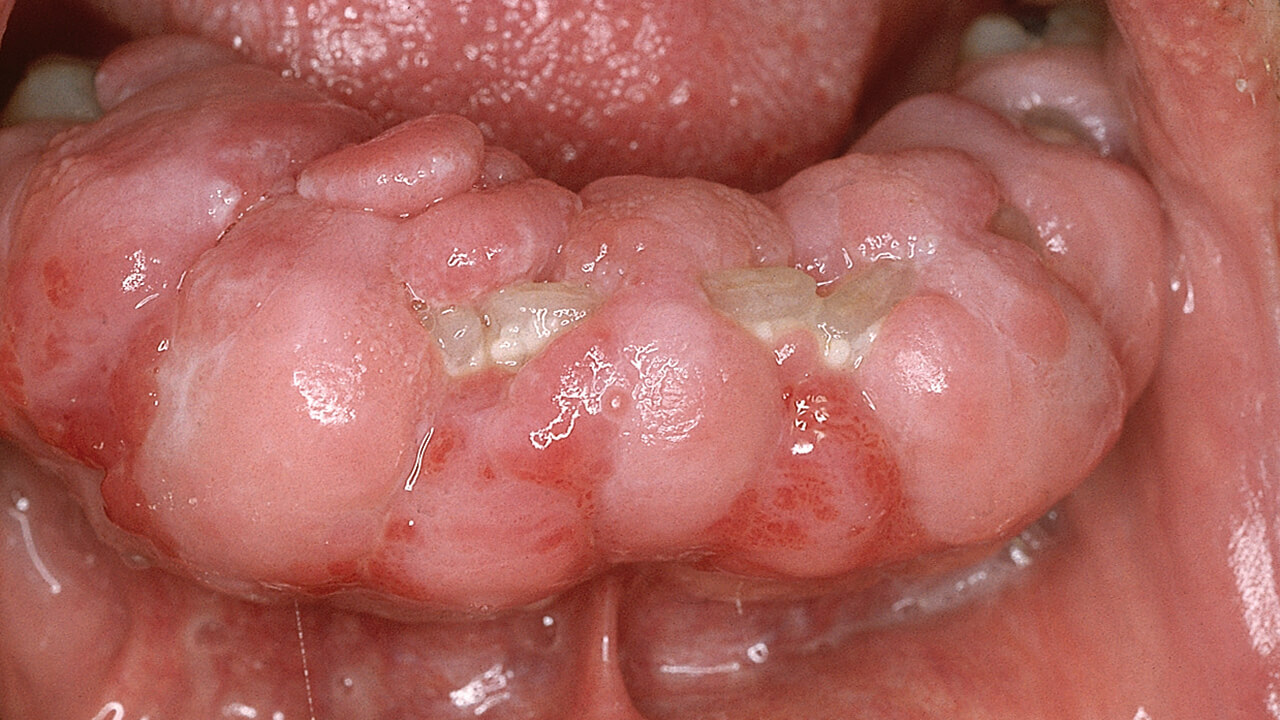
Poster 2689, Language: English, GermanKetteler, Judith / Poggenpohl, Laura / van der Bijl, Nils / Daume, LindaThe clinical diagnosis of gingival hyperplasia can have multiple causes, in which acquired and hereditary causes must be distinguished. Only pathohistologically can the true cell proliferation be distinguished from the increase in cell volume. With less than 100 known cases worldwide, Temple-Baraitser syndrome is a very rare hereditary, autosomal dominant genetic disorder. It is characterized by mental retardation, hypotonia in early childhood, epilepsy, small or non-existent thumb and toe nails, and certain facial features. Temple-Baraitser syndrome is caused by mutations in the KCNH1 genome at chromosomal locus 1q32.2. A ten-year-old female patient presented accompanied by her parents. Human genetics had shown that she had Temple-Baraitser syndrome. In all previously known cases of the syndrome, epileptic seizures and autistic behaviour were reported, as in this patient. The girl therefore also took Ospolot (anticonvulsant) daily. The patient showed the typical phenotype, with a low hairline, flat forehead, downward sloping palpebral fissures, broad, depressed nasal bridge with anteriorly directed nostrils, short columella, long philtrum, and high palate. The gingival hyperplasia typical of late childhood was also clearly evident in this patient. The patient had deciduous dentition with poor hygiene due to limited compliance and pronounced gingival hyperplasia. The permanent dentition was - as far as radiologically assessable - in place. The gingival hyperplasia in this patient is most likely syndrome- and anticonvulsant-associated. The treatment of gingival hyperplasia depends on the cause and usually consists of achieving the best possible hygiene of the dentition and, in individual cases, the removal of excess tissue. The family is therefore advised to improve oral hygiene. Further tooth eruption is awaited and orthodontic support is provided if necessary. Complete discontinuation of the medication is often not possible, as was the case with the anticonvulsants in this case.
Keywords: Temple-Baraitser syndrome, gingival hyperplasia, anticonvulsants
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 2/2025
Poster 2693, Language: English, GermanDaume, Linda / Jaber, Mona / Oelerich, Ole / Kleinheinz, JohannesOsteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a defect in type I collagen that leads to bone fragility and connective tissue disintegration. The orofacial manifestations of OI include dentinogenesis imperfecta (DI), tooth and jaw malocclusion, and dental anomalies.This case report shows a four-year-old female patient with OI who presented with brown discolouration typical of DI on all deciduous teeth on oral examination. The teeth were already severely abraded and the bite height was reduced. The patient was symptom-free and practiced optimised oral hygiene. Patients with these genetic structural anomalies require lifelong, close, interdisciplinary dental care to maintain the results of treatment.
Keywords: osteogenesis imperfecta, dentinogenesis imperfecta, rare genetic disorders
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 2/2025
Poster 2694, Language: English, GermanDaume, Linda / Kleinheinz, JohannesA patient with ectodermal dysplasia (ED) presented with a total of 20 congenital missing teeth, including wisdom teeth. An ED was confirmed by molecular genetic testing. An implant-supported denture for fixed, masticatory rehabilitation was applied for and approved by the health insurance company as an exceptional indication. The treatment was carried out after completion of orthodontic treatment at the age of 17. This means that patients with multiple missing teeth can receive an implant-prosthetic restoration before growth is complete. Patients demonstrably gain in quality of life.
Keywords: ectodermal dysplasia, implants, multiple agenesis
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 2/2025
Poster 2690, Language: English, GermanJaber, Mona / Daume, Linda / Hanisch, Marcel / Jung, Susanne / Jaber, MohammedThe aim of this study was to determine the extent to which pain reduction can be achieved by applying a new conservative treatment approach (from a neurological and dental perspective) for jaw and facial pain. 42 pain patients presented at the maxillofacial outpatient clinic after an unsuccessful search for a dental focus. The criteria were jaw and facial pain. Of these, 25 patients had previously undergone inpatient neurological assessment due to pain exacerbation. The patients were also categorized according to whether they were receiving neuroleptics. All patients were treated in the MKG according to the same protocol. All patients received a total of 2 questionnaires. One before therapy and the second after 6 weeks of wearing the splint. At the 1st session, the patient undergoes an osteopathic screening; the 1st session also includes a detailed anamnesis. During the 2nd session, osteopathic treatment is carried out while the bite is contactless using cotton rolls. The two main influences on the position of the temporomandibular joint are manipulated: the occlusion by means of cotton rolls and the osteopathic treatment of the masticatory muscles in particular. The bite is then taken directly without any manipulation. In the 3rd session, the osteopathic treatment is carried out first and then the splint is inserted. The patients had to wear the splint permanently for 6 weeks (except for food intake) for neuromuscular adaptation. The patients received physiotherapy during this phase. 6 weeks after wearing the splint, the patients were called in for the 1st splint check after osteopathic treatment. The 2nd questionnaire was now completed by the patients. The results: Eleven patients wore the splint at night and hourly during the day. The patients described relaxed masticatory muscles in the morning. The intensity of pain and the initial symptoms were reduced, but were still present. Of the 31 patients who adhered to the intensive wearing mode of the splint, 22 patients were free of symptoms and complaints. In the remaining 9 patients, the symptoms and complaints were still present, but were described as significantly reduced. Conclusion: Based on the 42 patients treated, it can be concluded that the therapeutic approach is promising for the treatment of jaw and facial pain.
Keywords: Jaw and facial pain, neurology, osteopathy, dental splint
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 2/2025
Poster 2695, Language: English, GermanDaume, Linda / Poggenpohl, Laura / Joanning, Theresa / Kleinheinz, JohannesLichen planus is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes (especially the oral and genital mucosa) and whose aetiology is unknown. Initially, topical salves, gels or mouthwashes containing corticosteroids are used for treatment. For localized, chronic ulcerative oral lichen planus lesions (OLP), an intralesional application of corticosteroids can be used, which can sometimes be repeated two to three times at intervals of just under a month. This case report shows that intralesional injection of triamcinolone is an effective treatment for refractory cases of OLP. Long-term and regular monitoring is required.
Keywords: oral lichen planus, ulcerativ lesions
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 2/2025
Poster 2698, Language: English, GermanOelerich, Ole / Menne, Max C. / Daume, Linda / Runte, Christoph / Becker, AlexanderObjective: Peri-implant bone loss is a significant parameter that determines the survival rate of implant-supported prosthetic restorations. The aim of this study is to compare the peri-implant bone level between the parallel technique commonly used in everyday practice and a modified right-angle technique. In particular, studies with long follow-up periods may be subject to projection-related deviations in the determination of radiological peri-implant bone loss. The following study investigates whether these projection-related deviations can be minimised by using a modified right-angle technique. Material and method: Three mandibular segments with a deviant bone course were printed from radio-opaque PLA (Nanovia PLA XRS, Nanovia) using a 3D printer (Ender 3v2, Creality), as was a modifiable bite block. A Straumann RC BL 4.1 x 12mm implant (Straumann) was then inserted into each model at the same location. A total of 15 radiographs were taken for each model and radiographic technique (parallel vs. right-angle) by two clinicians. Another clinician measured the maximum radiographic bone loss to the implant shoulder mesially and distally in each of the 90 radiographs. The measurements of the individual models were examined for variance homogeneity using a Levene test to determine how strongly the scatter of the results depends on the X-ray technique. Results: The Levene test showed that there was no variance homogeneity for the mesial measurements on model 2 and for the distal measurements on model 1, model 2, and model 3. The standard deviation was lower for the modified right-angle technique in each case. The measurements varied between the models (and measuring points) between 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm for the modified right-angle technique and between 0.3 mm and 0.7 mm for the parallel technique. Summary: In summary, it can be said that the modified right-angle technique can help to minimise the projection-related deviations between consecutive X-ray images.
Keywords: x-ray, projection-related deviation, peri-implant, bone loss
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 1/2025
Poster 2669, Language: English, GermanKöckerling, Nils / Oelerich, Ole / Daume, Linda / Kleinheinz, JohannesMarcus Gunn syndrome, or mandibulopalpebral synkinesis, is a congenital movement of the upper eyelid when the mouth is opened. The cause is a paradoxical ipsilateral innervation between the eyelid retractor and the lateral pterygoid muscle. Clinically, there is ptosis of the affected eyelid, which disappears when the mouth is opened. The inverse Marcus-Gunn phenomenon describes an ipsilateral closure of the eyelid when the lateral pterygoid muscle contracts. The combination of both phenomena is also known as ‘See-Saw’ Marcus Gunn syndrome. This is a congenital condition that leads to lifting of the upper eyelid on one side and lowering of the upper eyelid on the opposite side when the mouth is opened. This condition is considered an extreme rarity. In this case report, we show a twenty-year-old woman who has had the condition from birth. At rest, there is incomplete ptosis of the right eye. When the mouth is opened, the right eyelid lifts involuntarily and the left upper eyelid lowers almost completely. In addition, she shows a bilateral involuntary pupil movement to the left caudal side. A causal therapy is not yet known, genetic counselling is recommended. Therapeutic approaches relate to independent conscious training of the dysinervated eyelid in front of the mirror; in severe cases, surgical correction may be considered.
Keywords: MGS, rare phenomenon, mandibulopalpebral synkinesis
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 1/2025
Poster 2685, Language: English, GermanNafz, Ludwig / Daume, Linda / van der Bijl, Nils / Kleinheinz, JohannesThe cutaneous horn is a clinical finding rooted in a variety of different benign and malignant causes. Sampling with subsequent histologic examination is the diagnostic gold standard. Depending on the causing pathology, different therapies are necessary. We report a case in which a patient presented to our outpatient clinic with two cutaneous horns of the lower lip. A biopsy had already been performed in another clinic five years ago, in which a not fully excised, well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (G1), was found. The patient refused further surgical treatment recommendations at the time. Due to the size-progressive and functionally limiting findings, the patient presented to our clinic. After removal of the lesions, a histological examination was performed. Apart from verrucous hyperplastic squamous epithelium, no evidence of malignancy was histologically found. As there were no histologically visible signs of malignancy, the patient was discharged in an aesthetically and functionally acceptable state into a follow-up program with clinical check-ups every six months in order to detect and remove any recurrences at an early stage.
Keywords: cornu cutaneum, cateneous horn, squamous cell carcinoma, lower lip
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 1/2025
Poster 2686, Language: English, GermanJaber, Mona / Trento, Guilherme / Daume, Linda / Hanisch, Marcel / Kleinheinz, JohannesPrimary failure of eruption is a genetic partial eruption disorder that leads to an open posterior bite. The clinical severity and manifestation of primary failure of eruption are variable. The correct diagnosis of this eruptive anomaly plays an essential role in treatment planning, which can be prosthetic, orthodontic, surgical or multidisciplinary. The aim of this study was to determine the extent to which adequate treatment can be derived from the radiologic presentation of the PFE in the orthopantomogram. Preoperative panthomogram images were evaluated in 42 patients with confirmed PFE. The basis for treatment decisions was defined as follows: Evaluation of the affected teeth, evaluation of the bone, occlusal lines in the posterior region. Treatment can be standardised on the basis of orthopantomogram images in patients with PFE. We were able to derive the following treatment options from the orthopantomogram images: If the teeth are slightly below the occlusal plane, prosthetic treatment is indicated; in the case of a negative occlusal line in the mandible and also in the maxilla, extraction / augmentation / implantation / prosthetics should be selected as a treatment option; if the occlusal plane is displaced caudally in the mandible and cranially in the maxilla, a bimaxillary repositioning osteotomy would be indicated; if the occlusal plane is displaced caudally in the mandible and cranially in the maxilla, distraction or a segmental osteotomy with fixation would be indicated. The evaluation of orthopantomogram images of confirmed primary failure of eruption patients has shown that criteria can be defined that lead to standardisation and simplification of treatment.
Keywords: orthopantomogram, primary failure of eruption, PFE, treatment decisions, treatment standardised
International Poster Journal of Dentistry and Oral Medicine, 1/2025
Poster 2688, Language: English, GermanWerner, Julian / Köckerling, Nils / Kleinheinz, Johannes / Daume, LindaAcute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is an acute disease in which B-symptoms such as weakness, fever, and night sweats usually appear early in the case history. However, subtypes of AML can present with specific symptoms, for example in the form of gingival hyperplasia. Sampling (PE) with histological examination is considered the gold standard of diagnosis. We report a case in which a patient with gingival hyperplasia in region 17-13 presented in September 2023. The PE performed revealed the presence of a chloroma (syn. myeloblastoma or granulocytic sarcoma), which is the extramedullary manifestation of AML or an AML-related syndrome. The patient was then referred to the oncology day clinic. After further diagnostics, AML with an NPM1 mutation was detected and the patient was transferred to oncology treatment. A complete inspection and palpation of the oral cavity is essential for the early detection of (malignant) changes. In addition, systemic diseases often show oral manifestations as an initial or accompanying symptom. Here, the dentist can play a decisive role in quickly establishing the diagnosis. If lesions show no tendency to heal within two weeks despite adequate treatment, the previously made (suspected) diagnosis and the cytological or histological findings must be questioned and repeated if necessary.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukaemia, AML, oral manifestation