The stem cells ,PRP,CSF-1 and integrins-layering scaffolds on bone augmentation
The stem cells ,PRP,CSF-1 and integrins-layering scaffolds on bone augmentation
Category: Surgery, Implantology
Language(s): English
Publication year: 2009
Video source: 60 Jahre Quintessenz
Content
Bone cells equilibrium is a important for: embryonic
bone development, bone fracture healing and bone
substitutes transplantation. Modified bone graft by
incorporation of sialoprotein-derived EPRGNYR or RGD
cell attachment motif induced more bone in heterotopic
bone induction in rats. Several bone augmentation
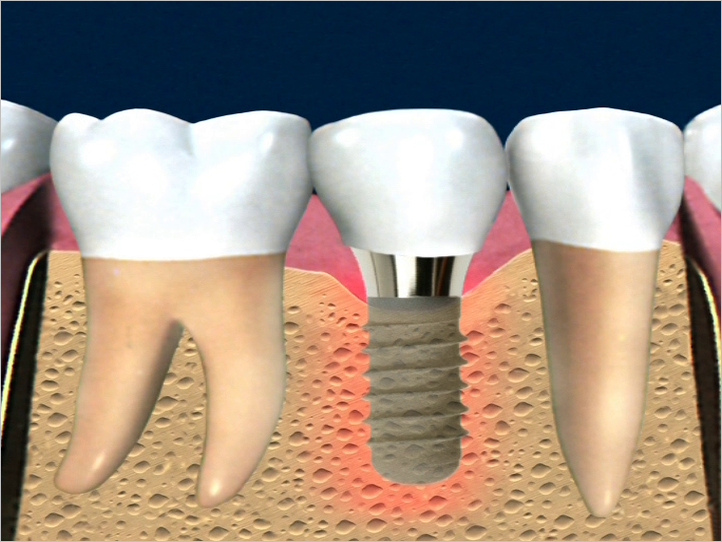
techniques were applied for alveolar bone formation
as a part of implant therapy. We compared the
efficacy of mature stem cells CD34+, bone cells precursor
versus platelet rich plasma (PRP) transplanted in
deficient bone sites on a carrier. CD34+ stem cells were
isolated in gradient ficoll/hypaque by centrifugation.
Isolation of platelet - for highly purify and concentrated
PRP was performed using Cobe-Spectra trombocytophoresis
from patients blood. The Fourier analysis of:
x-ray and histological pictures showed that 6 months
after surgery the augmented bone is in its trabecular
structure closest to the control-contralateral bone
under PRP/bovine mineral transplants in comparison to
stem cells CD34+, but 1 year after surgery - no differences
between intact and augmented sites were found.
It is suggested that growth and differentiated factors
were released during first days/weeks after transplantation
from PRP and quicker into local environment
(osteoblasts/osteoclasts, periosteal cells, blood cells)
than from the transplanted stem cells which first differentiate
into osteoclats in known "triad" methodology.