International Journal of Esthetic Dentistry (EN), 3/2024
The Last PagePubMed-ID: 39092824Seiten: 298, Sprache: EnglischGrunder, UeliInternational Journal of Esthetic Dentistry (DE), 3/2024
The Last PageSeiten: 316, Sprache: DeutschGrunder, UeliImplantologie, 4/2023
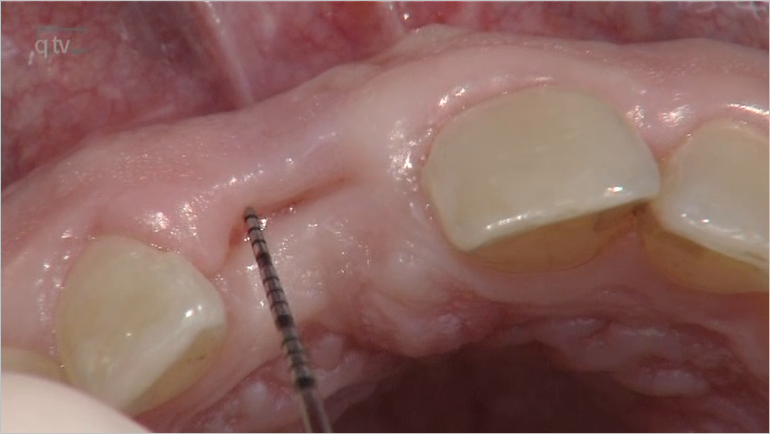
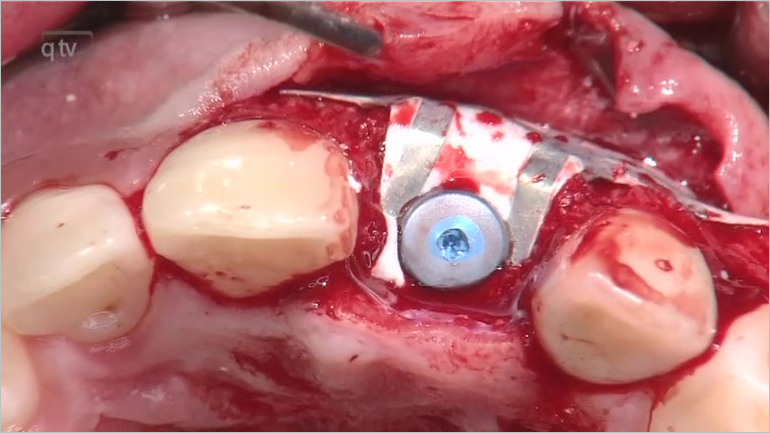
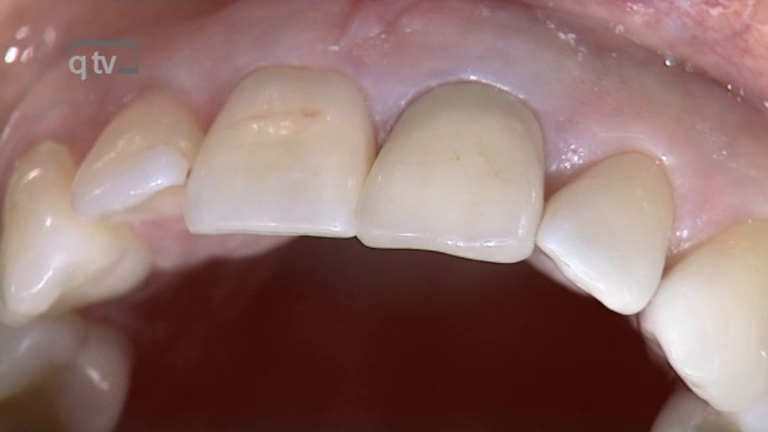
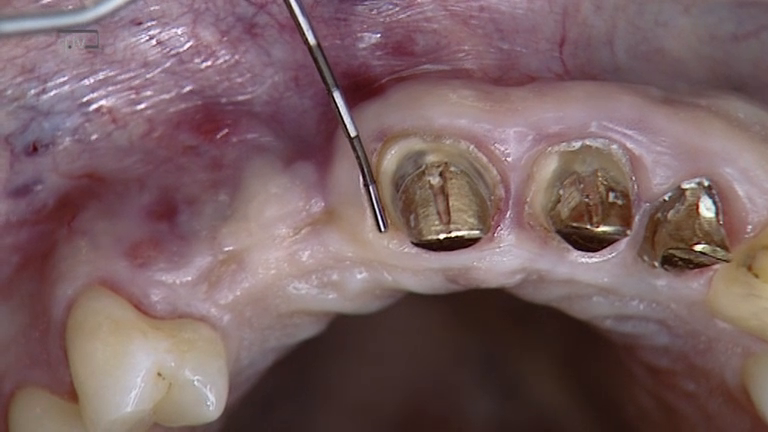
Seiten: 399-410, Sprache: DeutschGrunder, Ueli / Schupbach, PeterEin klinischer BerichtAnhand von klinischen Fällen zeigt sich, dass nach dem Einsetzen von subepithelialen Bindegewebetransplantaten das Weichteilgewebe bei bestimmten Patienten langfristig massiv an Dicke zunimmt. Dies kann wissenschaftlich derzeit nicht erklärt werden. Dieser Artikel beschreibt, wie wenig wir gegenwärtig die genauen Vorgänge tatsächlich verstehen.
Manuskripteingang: 14.09.2023, Annahme: 14.10.2023
Schlagwörter: Implantate, Weichgewebeaugmentation, subepitheliales Bindegewebetransplantat, Langzeitresultate
International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 5/2017
Seiten: 627, Sprache: EnglischGrunder, UeliImplantologie, 4/2017
Seiten: 369-377, Sprache: DeutschWeng, Dietmar / Grunder, UeliEin Fall, wie er im Buche stehtIm vorliegenden Artikel nehmen die Autoren Bezug auf einen in der ersten Ausgabe der Zeitschrift IMPLANTOLOGIE vor 25 Jahren veröffentlichten Fall zweier zentraler Oberkieferfrontzahnimplantate. Der Fall ist seit Eingliederung der Implantatkronen über 27 Jahre nachdokumentiert. Es wird anhand dieses Beispiels diskutiert, was im Jahre 2017 anders gemacht werden würde als in den Jahren 1990 bis 1992. Anhand dieser Diskussion werden Entwicklungen und deren Hintergründe deutlich gemacht, die für Implantatversorgungen im ästhetischen Bereich klinisch relevant sind, um eine Langzeitstabilität von Hart- und Weichgeweben zu erzielen. Dazu zählen unterschiedliche Operationstechniken und das zeitliche Vorgehen, Inzisionstechniken in der ästhetischen Zone, die Anwendung von Bindegewebetransplantaten sowie die Unterschiede zwischen zementierten und verschraubten Implantatsuprastrukturen.
Schlagwörter: Fallbericht, Frontzahnimplantat, ästhetische Zone, Langzeitergebnis, Erfolgsfaktor, operatives Vorgehen, Inzision, Bindegewebetransplantat, Zementierung, Verschraubung
Quintessenz Zahnmedizin, 10/2012
Tipps für die PraxisSeiten: 1331-1335, Sprache: DeutschGrunder, UeliInternational Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 6/2011
PubMed-ID: 22140663Seiten: 613-620, Sprache: EnglischGrunder, Ueli / Wenz, Birgit / Schupbach, PeterThe objective of this case series was to evaluate the clinical and histologic outcome of guided bone regeneration around simultaneously placed implants in sites with missing buccal bone walls. Eight weeks after tooth extraction, implants were inserted, and the sites were augmented in both the horizontal and vertical dimensions using a mineralized collagen bone substitute and a nonresorbable titanium-reinforced membrane. Six months later, small hard tissue biopsy specimens were harvested from the buccal bone walls at approximately mid-height of the original defect. The histologies revealed ongoing bone formation. Clinically, an adequate amount of hard and soft tissue volume had formed.
International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 1/2011
PubMed-ID: 21365022Seiten: 9-17, Sprache: EnglischGrunder, UeliThe esthetic outcome of an implant-supported restoration is first of all dependent on the soft tissue volume. Since the labial bone plate resorbs in every direction after tooth extraction, even when an implant is placed immediately, most patients end up with compromised esthetics. Twenty-four patients were treated consecutively with implants placed in the maxillary anterior area at the time of tooth extraction using two different treatment modalities. The first 12 patients were treated without raising a flap, whereas a subepithelial connective tissue graft was placed using the tunnel technique in the labial area of the subsequent 12 patients at the time of tooth extraction and implant placement. The dimension of the labial volume was measured before treatment and 6 months after implant placement. The results show an average loss of volume in the nongrafted group of 1.063 mm, whereas in the grafted group, there was a slight gain of 0.34 mm. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of placing a soft tissue graft at the time of immediate implant placement in the esthetic zone.
International Journal of Esthetic Dentistry (EN), 2/2010
PubMed-ID: 20589260Seiten: 158-170, Sprache: EnglischGrunder, Ueli / Spielmann, Hans-Peter / Snétivy, DanielThe use of small-diameter implants is indicated when small missing teeth have to be replaced, especially in esthetic zones. Nevertheless, the small diameter can pose a limiting factor with respect to what materials can be used for the final crown. In most cases, full-ceramic crowns in combination with a ceramic abutment are usually the material of choice for final reconstructions. To date, based on mechanical considerations, a 3.5 mm implant diameter has been a contraindication for using ceramic abutments. The authors describe here the development, in vitro testing, and clinical use of a zirconium abutment with a 3.5 mm diameter. The advantages of this small-diameter zirconia abutment include a minimum platform height that offers optimal prosthetic flexibility, and an accurate transfer of the implant position on to the master model. Furthermore, a precise rotational orientation for single-tooth restorations, optimal mechanical stability, and optimal fatigue resistance can be achieved. The microgap is minimized and protection against overload is afforded. In the reported case, high patient satisfaction was achieved due also to an esthetically pleasing final result.