International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, Pre-Print
ScienceDOI: 10.3290/j.ijcd.b5638066, PubMed-ID: 3907311929. Juli 2024,Seiten: 1-64, Sprache: EnglischSzmukler-Moncler, Serge / Savion, Ariel / Sperber, Rasmus / Kolerman, Roni / Beuer, FlorianAim: To report on a novel digital superimposition workflow that enables measuring the supra-crestal peri-implant soft tissue dimensions all along implant treatment and afterwards. Materials and Methods: A preoperative CBCT and intra-oral scans (IOS) are successively taken before surgery, at the end of the healing period, at prosthesis delivery, and over time; they are digitally superposed on a dedicated software. Then, the stereolithography files (STL) of the healing abutment, of the prosthetic abutment and the crown are successively merged into the superposition set of IOSs. Result: The workflow protocol of merging successively the STL of each item into the superposition set of IOSs enables capturing the dimensions of the height and width of the supra-crestal soft tissues, at every level of the healing abutment, the prosthetic abutment and the crown. In addition, it allows measuring the vertical distance that the crown exerts pressure on the gingiva and the thickness of the papillae at every level of the abutment. Conclusion: This novel digital superimposition workflow provides a straightforward method of measuring the vertical and horizontal dimensions of the supra-crestal peri-implant soft tissues, including the papillae, at each stage of the implant treatment process. It allows investigating a certain number of soft tissue variables that were previously inaccessible to clinical research. It should help enhancing our comprehension of the peri-implant soft tissue dynamics.
Schlagwörter: CBCT, clinical research, digital merging, gingival height, gingival width, intra-oral scan, papilla, peri-implant soft tissues
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, Pre-Print
ScienceDOI: 10.3290/j.ijcd.b5951413, PubMed-ID: 3987180528. Jan. 2025,Seiten: 1-50, Sprache: EnglischAmer, Safwan / Szmukler-Moncler, Serge / Savion, Ariel / Damaskos, Thilo / Sperber, Rasmus / Beuer, FlorianAim: To compare the effect of the shape of the healing abutment, concave or straight, on the dimensions of the soft tissue after healing. Materials and methods: Patients needing implant therapy in the posterior area were treated with a 1-stage surgery protocol; concave (CONC) or straight (STR) healing abutments were randomly assigned after implant installation. Before surgery, a CBCT and an intra-oral scan were obtained (IOS#0); IOS#1 was taken after soft tissue healing. The CBCT, IOSs and STL of the abutments were merged; this allowed measuring the gained/lost gingival height (ΔH), the gingival width (GWAbut) and the emergence angles (ANG) of each group. Results: Twenty-seven implants (Ø 4.2 mm, SEVEN (MIS)) with 14 CONC and 13 STR healing abutments were available for analysis. ΔH of both groups did not differ statistically. The marginal gingiva of CONC either stayed within the abutment concavity (CONCin) or reached its straight portion beyond the concavity (CONCup). When GWAbut and ANG were measured without considering this feature, the differences between STR and CONC were not statistically significant. In contrast, once this feature was considered, the difference between the groups became statistically significant. For GWAbut, results were CONCup>STR>CONCin; for ANG it was STR≈CONCup>CONCin. Conclusion: Abutment shape did not affect the gingival height. Thickness of the gingiva at the concave abutment depended upon the position of the marginal gingiva, within or beyond the concavity. This exploratory pilot study might suggest that concave abutment height should be carefully chosen to ensure that the marginal gingiva reaches the level beyond the concavity.
Schlagwörter: CBCT, concave abutment, digital workflow, emergence angle, intra-oral scan, straight abutment, thickness of gingiva
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, Pre-Print
ScienceDOI: 10.3290/j.ijcd.b5951419, PubMed-ID: 3987177028. Jan. 2025,Seiten: 1-12, Sprache: EnglischSchütze, Plamena / Beuer, Florian / Bumann, AxelAim: This study aimed to evaluate OccluSense's reliability against conventional articulating films in assessing static occlusion. The study also targets to identify possible limitations and influencing factors when using this device to asses static occlusion. Materials and methods: This experimental research utilized twenty epoxy resin typodont models representing various occlusal discrepancies. They were mounted in a CP Artex articulator, and static occlusion was assessed in maximum intercuspal position using shimstock foil as a gold standard. The digitally generated occlusograms by OccluSense were compared with conventional occlusal indicators, including 40 μm articulating paper (AP) and 12μm articulating foil (AF). Intrarater Reliability was assessed using Cohen's kappa coefficient (κ). Result: AP and AF showed high reliability, with κ values of 0.94 and 0.93 respectively, indicating almost perfect agreement with the gold standard. In contrast, OccluSense demonstrated an overall reliability of κ = 0.22, signifying fair agreement. Notably, significant discrepancies in κ values were observed among different malocclusions, with deep bite exhibiting the lowest reliability at κ = 0.02, representing poor agreement (P<0.05). Conclusion: OccluSense is less reliable compared to traditional methods, such as articulating paper, for assessing static occlusion. Its limitations are particularly evident in patients with deep bite, making it unsuitable as a standalone tool at the present time.
Schlagwörter: Articulating paper, Dental occlusion, Digital occlusogram, OccluSense, shimstock foil
Deutsche Zahnärztliche Zeitschrift, 3/2025
BuchbesprechungSeiten: 178-179, Sprache: DeutschBeuer, Florianvon Otto Zuhr und Marc HürzelerQZ - Quintessenz Zahntechnik, 3/2025
ErfahrungsberichtSeiten: 242-248, Sprache: DeutschSchmidt, Franziska / Beuer, Florian / Unkovsky, Alexey3D-Druck hat in der Zahnmedizin Fortschritte gemacht, und auch die Herstellung von vollkeramischen Restaurationen mit dem 3D-Drucker schreitet voran. Besonders Methoden mit UV-polymerisierbaren Harzen zeichnen sich durch eine hohe Präzision und Komplexität aus, was besonders für Non-prep-Restaurationen von Interesse ist. Die LCM-Technologie erlaubt die Herstellung ultradünner Veneers mit hoher Passgenauigkeit. Die Eignung wurde bereits in klinischen Fällen gezeigt.
Schlagwörter: CAD/CAM, additive Fertigung, minimal-invasiv, Veneers, Lithiumdisilikat
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, 2/2025
EditorialDOI: 10.3290/j.ijcd.b6336051Seiten: 95-97, Sprache: Englisch, DeutschBeuer, FlorianThe Journal of Adhesive Dentistry, 1/2025
Open Access Online OnlyClinical ResearchDOI: 10.3290/j.jad.c_210619. Juni 2025,Seiten: 123-136, Sprache: EnglischMayinger, Felicitas / Lankes, Valerie / Roos, Malgorzata / Rohr, Nadja / Ioannidis, Alexis / Elsayed, Adham / Güth, Jan-Frederik / Edelhoff, Daniel / Passia, Nicole / Esmail, Iman / Beuer, Florian / Wolfart, Stefan / Spies, Benedikt Christopher / Schimmel, Martin / Abou-Ayash, Samir / Hahnel, Sebastian / Schlenz, Maximiliane Amelie / Frankenberger, Roland / Blunck, Uwe / Kraus, Dominik / Engelschalk, Marcus / Huettig, Fabian / Kern, Matthias / Luehrs, Anne-Katrin / Gierthmuehlen, Petra C. / Stawarczyk, BognaPurpose: To investigate, via questionnaire, how protocols for adhesive luting workflows of dental restorations are applied in three German-speaking countries. Material and Methods: A 47-item questionnaire gathered data on airborne particle abrasion (APA) unit characteristics, parameters, operating procedures, pretreatments in adhesive luting workflows for restorations, and participant demographics. The survey was distributed via trade journals, expert associations, universities, technical schools, and social media. Marginal absolute and relative frequencies were analyzed (95% confidence intervals), with Chi-squared tests comparing observed and expected frequencies (P0.05). Twenty-three experts voted on 23 recommendations regarding APA parameters and other pretreatments for bonding restorations. Results: A total of 267 participants completed the survey. Access to an APA unit was linked to a higher likelihood of performing APA before placement. Approximately half of the participants used APA in their practice. For zirconia restorations, 47.2% applied alumina APA at 50 µm/0.1 MPa, while 36.7% used the same settings for polymer-based restorations. For alloys, 37.5% employed 110 µm/0.2 MPa. These preferences correlated with age (≥30 years), experience (≥10 years), profession (dental technician/dentist), prior instruction/training, and daily APA use. Adhesives with MDP were used for zirconia (63.8%) and those with silane for silicate-based ceramics (55.9%). Agreement on recommendations ranged between 52% and 100%, with 21/23 reaching an average of 93%. Conclusion: Access to APA influenced clinical decisions and the feasibility of adhesive luting workflows. Adequate APA equipment in dental facilities is essential for quality care. Standardized protocols, training, and education across dental professions are necessary to enhance understanding and proper use of APA.
Schlagwörter: adhesive dentistry, airborne particle abrasion, parameter, surface conditioning, bonding, dental restoration
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, 1/2025
DOI: 10.3290/j.ijcd.b6120402, PubMed-ID: 40178298Seiten: 3-5, Sprache: Englisch, DeutschBeuer, FlorianImplantologie, 4/2024
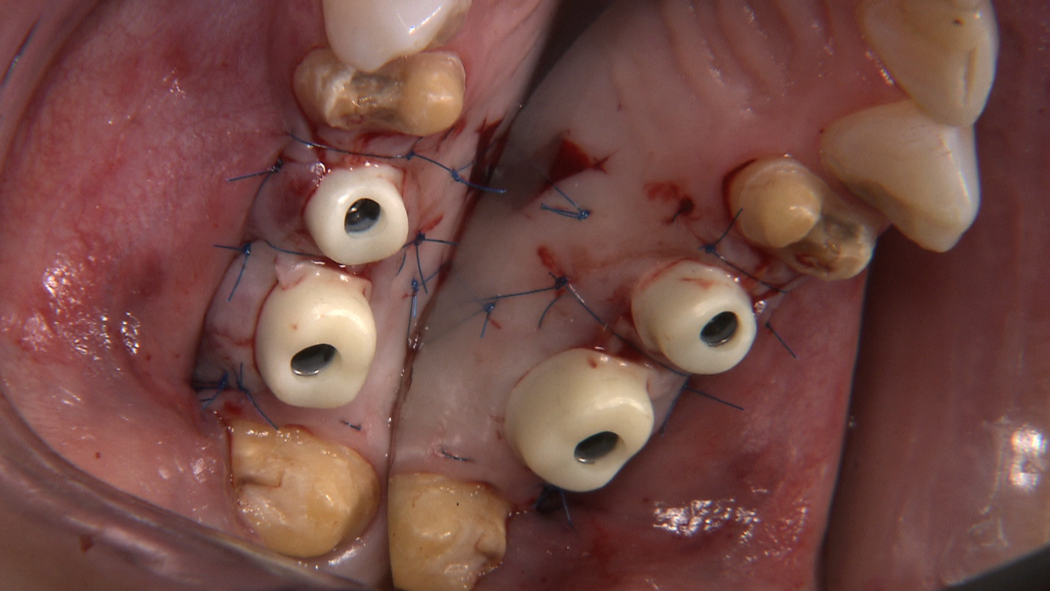
Seiten: 415-432, Sprache: DeutschHildebrand, Detlef / Gärtner, Florian / Rosinski, Andrea / Jäckel, Timo / Siebert, Heiko / Kunz, Andreas / Beuer, FlorianEin Überblick aus der PraxisDie Behandlung prospektiv zahnloser Patienten mit dentalen Implantaten stellt die Zahnärzte auch heute vor große Herausforderungen vor, während und nach der chirurgischen Phase. Die Behandlungsplanung und deren Umsetzung sind von essenzieller Bedeutung, um den klinischen Behandlungserfolg zu garantieren. Anhand einer fundierten Analyse der Ausgangssituation werden im vorliegenden Beitrag die notwendigen Behandlungsschritte vollumfänglich skizziert, in den klinischen Ablauf integriert und umgesetzt. Dabei spielen für die Behandlung des zahnlosen Kiefers grundsätzliche Entscheidungen eine große Rolle: (1) „In welchem Umfang müssen Extraktionen erfolgen?“, (2) „Kann eine sofortige Implantation (Sofortimplantation) erfolgen?“ und (3) „Kann eine zeitgleiche prothetische Versorgung (Sofortversorgung) umgesetzt werden?“. Das Behandlungsteam, bestehend aus Implantologe/Chirurg, Prothetiker und Zahntechniker, funktioniert umso besser und effektiver, je besser die Behandlungsabläufe analog und digital miteinander abgestimmt sind und diese im Sinne eines zielgerichteten Workflows funktionieren. In diesem Artikel werden digitale Hilfsmittel im Bereich der Planung, Platzierung und Weiterentwicklungen moderner Implantatsysteme beleuchtet, die das implantologische Team unterstützen können. Neue Implantate mit speziellen Schraubendesigns helfen nicht nur, die Primärstabilität nach Einbringung in den Knochen vor der initialen Sofortbelastung zu verbessern, sondern ermöglichen mit kurzen bzw. extrakurzen Implantatlängen (8 mm) auch im atrophierten Seitenzahnbereich zahnloser Ober- und Unterkiefer, die klassischen „All-on-X“-Konzepte („All-on-4“) zu erweitern bzw. zu vereinfachen („Fix-on-X“). Anhand von beispielhaften Patientenfällen werden diese aktuellen Konzepte veranschaulicht und anhand der klinischen Daten diskutiert.
Schlagwörter: All-on-4, Fix-on-X, Sofortimplantation, Sofortbelastung, Sofortversorgung, Implantate mit aggressivem Gewinde, Primärstabilität, kurze Implantate, beschleunigte Regeneration
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, 4/2024
ScienceDOI: 10.3290/j.ijcd.b4451424, PubMed-ID: 37823541Seiten: 379-388, Sprache: Englisch, DeutschPrause, Elisabeth / Schmidt, Franziska / Unkovskiy, Alexey / Beuer, Florian / Hey, JeremiasZiel: Die Anpassung und Übertragung einer stabilen Okklusion kann bei prothetischen Rehabilitationen eine große Herausforderung darstellen. Ziel der vorliegenden Studie war es, eine nicht-invasive Behandlungsoption für komplexe prothetische Rehabilitationen und Okklusionsanalysen mittels 3-D-gedruckter Restaurationen klinisch zu bewerten. Material und Methode: Elf Patienten erhielten eine teilweise oder vollständige Rehabilitation mithilfe von 3-D-gedruckten Restaurationen (n = 171). Nach 12 Monaten klinischen Einsatzes wurden alle Restaurationen anhand der Kriterien des United States Public Health Service (USPHS) analysiert. Ergebnisse: Die klinischen Daten nach 12 Monaten zeigten, dass 3-D-gedruckte Restaurationen eine Überlebensrate von 84,4 % aufwiesen. Komplikationen traten meist in Bezug auf die anatomische Form (7 %) oder die marginale Integrität (6 %) auf und wurden folglich mit „Charlie“ oder „Delta“ bewertet. Die Farbstabilität und Farbübereinstimmung der 3-D-gedruckten Restaurationen wurde bei 83 % bzw. 73 % aller Restaurationen mit „Alpha“ bewertet. Die marginale Entzündung wurde bei 89 % aller Restaurationen mit „Alpha“ bewertet. Es wurden eine ausgezeichnete Oberflächentextur und keine Sekundärkaries oder postoperativen Sensibilitäten (100 %) beobachtet. Schlussfolgerungen: 3-D-gedruckte Restaurationen könnten eine alternative Behandlungsoption für die Einleitung komplexer prothetischer Rehabilitationen sein. Technische Komplikationen traten nur selten auf. Biologische Komplikationen traten überhaupt nicht auf. Die Farbstabilität zeigte nach 12 Monaten klinischen Einsatzes vielversprechende Ergebnisse. Die Ergebnisse sind jedoch mit Vorsicht zu interpretieren. Langzeitergebnisse mit einer hohen Anzahl von Versorgungen sollten abgewartet werden.
Schlagwörter: 3-D-Druck, additive Fertigung, Farbstabilität, Verschleißverhalten, in vivo, CAD/CAM