The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, Pre-Print
DOI: 10.11607/jomi.1138424. Juni 2025,Seiten: 1-26, Sprache: EnglischPeppmeier, Sandra Marina / Henn, Paul / Graf, Tobias Gust / Gehrke, Peter / Neugebauer, Jörg / Henn, PaulObjectives: This retrospective study aimed to evaluate peri-implant marginal bone level changes and radiographic grayscale value (GSV) alterations in vertically compromised bone around ultra-short implants (5.2 mm) placed in native bone compared to standard-length implants (8–14 mm) placed in augmented sites. Methods: The mean follow-up period was 38 months, with a maximum of 64 months. A total of 53 patients, collectively receiving 131 implants, were included. Each patient received at least both one ultra-short implant and one standard-length implant. In total 78 short implants and 53 standard length implants were placed. Standard-length implants were predominantly placed using alveolar ridge augmentation with autologous bone chips, sinus lifting, or retromolar bone block grafting. Autologous bone chips were supplemented with up to 50% bone substitute materials. Peri- implant marginal bone levels were assessed using the Distance Implant to Bone (DIB) method, while radiographic GSV served as a surrogate for bone density. All radiographic measurements were performed by two blinded evaluators using an automated x-ray overlay protocol, achieving high inter-rater reliability (intraclass correlation coefficients > 0.98). A linear mixed model, accounting for heterogeneous follow-up intervals, was applied to estimate changes in marginal bone levels (ΔMBL) and grayscale values (ΔGSV) (p < 0.05). Results: The mean follow-up period was 38 months, with a maximum of 64 months. A total of 123 implants were assessed for changes in marginal bone level and grayscale values, representing bone density. Ultra-short implants demonstrated significantly lower marginal bone loss over the observation period (ΔMBL = −0.61 ± 0.93 mm) than standard-length implants placed in augmented bone (ΔMBL = −1.11 ± 1.26 mm; p = 0.001). Moreover, ∆GSV around ultra-short implants significantly increased (ΔGSV = 3.26 ± 20.52 a.u), whereas standard-length implants exhibited a decrease in radiographic density (ΔGSV = −0.76 ± 21.59 a.u; p = 0.009). Conclusions: Within the limitations of this mid-term retrospective study, ultra-short implants placed in native bone exhibited statistically superior marginal bone preservation and significantly increased radiographic density when compared to standard-length implants placed in augmented sites. These results help to underscore the potential clinical advantage of opting for ultra-short implants in suitable native bone conditions to reduce the morbidity associated with extensive augmentation and less risk for periimplantitis on the long-term run in selected cases. Nevertheless, further long term, randomized investigations are warranted to confirm these findings.
Schlagwörter: Dental implants, Bone density, Grayscale value, Implant length, Bone augmentation, Marginal bone level
The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 2/2025
DOI: 10.11607/jomi.10574, PubMed-ID: 39485909Seiten: 188-196, Sprache: EnglischHenn, Paul / Gehrke, Peter / Happe, Arndt / Neugebauer, JörgPurpose: To conduct a retrospective study on the marginal bone level (MBL) of reduced diameter implants (RDIs) to analyze them in the context of various surgical and prosthetic treatment strategies using heterogeneous data from a private practice. Materials and Methods: A total of 123 patients were treated with 326 implants. Of those implants, 247 of them were RDIs, and the remaining 79 implants were standard-diameter implants (SDIs) as patient-related controls. The mean observation time was 24.4 months, and the maximum observation time 76.0 months. The peri-implant bone level of the implants was evaluated, while considering the diameter, time of implant placement, time of loading, extent of augmentation, and localization of the implants. The data were evaluated after restructuring using a mixed model analysis. Results: No significant difference was found between the use of RDIs or SDIs in the analyzed indications. Furthermore, no significant difference was found for the implant placement time, loading time, or the use of two-stage augmentations regarding the stability of the peri-implant bone level. Conclusions: Reduced-diameter implants are a sufficient treatment option in horizontally deficient bone conditions. The use of RDIs in the posterior region shows promising results; 3.5-mm- diameter implants may be indicated considering the individual patient situation. The use of a mixed model analysis for the evaluation of heterogeneous practice data can lead to a significant increase in the number of retrospective studies and data integration from practices, forming a sound basis for evidence-based dentistry.
Schlagwörter: bone augmentation, dental implants, implant diameter, marginal bone level, mixed model analysis
QZ - Quintessenz Zahntechnik, 6/2024
FallstudieSeiten: 608-617, Sprache: DeutschAdler, Stephan / Kistler, Steffen / Kistler, Frank / Frank, Ingo / Neugebauer, JörgAltersgerechte, langfristige Implantatversorgung im OberkieferDer Fallbericht zeigt anhand einer Fullarch- Implantatbrücke im Oberkiefer eines älteren Patienten das Potenzial digitaler Zahntechnik. Dargestellt werden die einzelnen Phasen von der interdisziplinären Planung gemeinsam mit dem Zahnarzt über das Provisorium bis zur definitiven Versorgung mit einer bemalten Zirkonbrücke. Wichtig für die Zufriedenheit des Patienten sind verlässliche Vorhersagen, Zeitund Kosteneffizienz und ein hoher Patientenkomfort. Die gleichbleibend hohe Präzision der digitalen Verfahren und Komponenten bieten dafür entscheidende Vorteile.
Schlagwörter: Zirkonoxid, digitaler Workflow, interdisziplinär, Implantatprothetik, festsitzende Versorgung
Implantologie, 4/2024
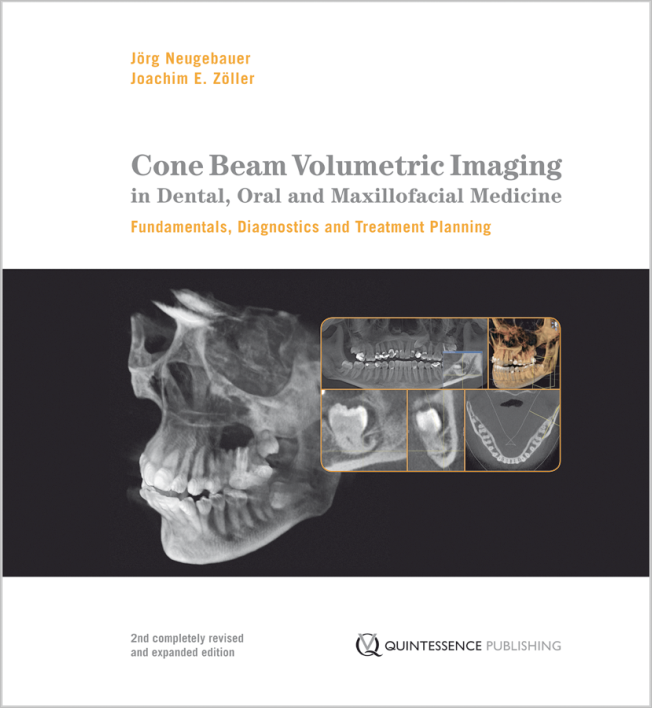
Seiten: 383-394, Sprache: DeutschNeugebauer, Jörg / Ritter, Lutz / Kistler, Steffen / Kistler, Frank / Dhom, Günter / Scheer, MartinDie digitale Planung und Diagnostik in der Zahnmedizin, insbesondere im Bereich der Implantologie, hat in den letzten Jahren erhebliche Fortschritte gemacht. Die dreidimensionale Bildgebung ist, vor allem durch die digitale Volumentomografie (DVT), zu einem hilfreichen Instrument für die genaue Positionierung von Implantaten, die Anwendung minimal invasiver Techniken und die Planung von Knochenaufbaumaßnahmen geworden. Die DVT bietet zwar eine höhere diagnostische Genauigkeit, ist aber im Vergleich zur herkömmlichen zweidimensionalen Bildgebung mit einer höheren Strahlendosis verbunden. Moderne DVT-Geräte bieten verschiedene Einstellungen, um eine indikationsbedingte Bildgebung bei minimaler Strahlenbelastung zu erhalten. Die DVT wird bei verschiedenen klinischen Indikationen wie der CAD/CAM-unterstützen Augmentationschirurgie und der Navigationschirurgie, die eine minimalinvasive Implantatinsertion ermöglichen, genutzt. Angesichts der höheren Strahlendosis ist es wichtig, die individuellen Einstellungsparameter so zu wählen, dass der diagnostische und therapeutische Nutzen höher als das mögliche Risiko ist. Die effektive Umsetzung dieser Technologien erfordert Schulungen und die Einrichtung standardisierter Arbeitsabläufe, um die Behandlungsergebnisse zu verbessern und die Morbidität der Patienten zu verringern.
Schlagwörter: DVT, minimalinvasive Implantattherapie, Navigationsschablone, Strahlenbelastung
The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 7/2023
SupplementDOI: 10.11607/jomi.10411, PubMed-ID: 37436948Seiten: 37-45o, Sprache: EnglischSchoenbaum, Todd R / Karateew, E Dwayne / Schmidt, Angela / Jadsadakraisorn, Chaniun / Neugebauer, Jörg / Stanford, Clark MPurpose: To quantify the cumulative oral implant survival rates and changes in radiographic bone levels based on the configuration of the implant-abutment connection type over time.
Materials and Methods: An electronic literature search was conducted in four databases (PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Embase), and records were refereed by two independent reviewers based on the inclusion criteria. Data from included articles were grouped by implant-abutment connection type into four categories ([1] external hex; [2] bone level, internal, narrow cone < 45 degrees; [3] bone level, internal wide cone ≥ 45 degrees or flat; and [4] tissue level) and duration of follow-up (short-term 1 to 2 years, mid-term 2 to 5 years, and long-term > 5 years). Meta-analyses were performed for cumulative survival rate (CSR) and changes in marginal bone level (ΔMBL) from baseline (loading) to last reported follow-up. Studies were split or merged as appropriate based on the implants and follow-up duration in the study and trial design. The study was compiled under PRISMA 2020 guidelines and registered in the PROSPERO database.
Results: A total of 3,082 articles were screened. Fulltext review of 465 articles resulted in a total of 270 articles (representing 16,448 subjects with 45,347 implants) included for quantitative synthesis and analysis. Mean ΔMBL (95% CI) was as follows: short-term external hex = 0.68 mm (0.57, 0.79); short-term bone level, internal, narrow cone < 45 degrees = 0.34 mm (0.25, 0.43); short-term bone level, internal wide cone ≥ 45 degrees = 0.63 mm (0.52, 0.74); short-term tissue level = 0.42 mm (0.27, 0.56); mid-term external hex = 1.03 mm (0.72, 1.34); mid-term bone level, internal, narrow cone < 45 degrees = 0.45 mm (0.34, 0.56); mid-term bone level, internal wide cone ≥ 45 degrees = 0.73 mm (0.58, 0.88); mid-term tissue level = 0.4 mm (0.21, 0.61); long-term external hex = 0.98 mm, 0.70, 1.25); long-term bone level, internal, narrow cone < 45 degrees = 0.44 mm (0.31, 0.57); long-term bone level, internal wide cone ≥ 45 degrees = 0.95 mm (0.68, 1.22); and long-term tissue level = 0.43 mm (0.24, 0.61). CSRs (95% CI) were: short-term external hex = 97% (96%, 98%); short-term bone level, internal, narrow cone < 45 degrees = 99% (99%, 99%); short-term bone level, internal wide cone ≥ 45 degrees = 98% (98%, 99%); short-term tissue level = 99% (98%, 100%); mid-term external hex = 97% (96%, 98%); mid-term bone level, internal, narrow cone < 45 degrees = 98% (98%, 99%); midterm bone level, internal wide cone ≥ 45 degrees = 99% (98%, 99%); mid-term tissue level = 98% (97%, 99%); long-term external hex = 96% (95%, 98%); long-term bone level, internal, narrow cone < 45 degrees = 98% (98%, 99%); long-term bone level, internal wide cone ≥ 45 degrees = 99% (98%, 100%); and long-term tissue level = 99% (98%, 100%).
Conclusion: The configuration of the implant-abutment interface has a measurable effect on the ΔMBL over time. These changes can be observed over a period of at least 3 to 5 years. At all measured time intervals, similar ΔMBL was noted for external hex and internal wide cone ≥ 45-degree connections, as were internal, narrow cone < 45-degree and tissue-level connections.
Schlagwörter: abutment, bone level, bone loss, connection, failure, implant, review, survival
The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, 7/2023
SupplementDOI: 10.11607/jomi.10500, PubMed-ID: 37436947Seiten: 30-36, Sprache: EnglischNeugebauer, Jörg / Schoenbaum, Todd R / Pi-Anfruns, Joan / Yang, Min / Lander, Bradley / Blatz, Markus B / Fiorellini, Joseph PPurpose: To evaluate the performance of one- and two-piece ceramic implants regarding implant survival and success and patient satisfaction.
Materials and Methods: This review followed the PRISMA 2020 guidelines using PICO format and analyzed clinical studies of partially or completely edentulous patients. The electronic search was conducted in PubMed/MEDLINE using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) keywords related to dental zirconia ceramic implants, and 1,029 records were received for detailed screening. The data obtained from the literature were analyzed by single-arm, weighted meta-analyses using a random-effects model. Forest plots were used to synthesize pooled means and 95% CI for the change in marginal bone level (MBL) for short-term (1 year), mid-term (2 to 5 years), and long-term (over 5 years) follow-up time intervals.
Results: Among the 155 included studies, the case reports, review articles, and preclinical studies were analyzed for background information. A meta-analysis was performed for 11 studies for one-piece implants. The results indicated that the MBL change after 1 year was 0.94 ± 0.11 mm, with a lower bound of 0.72 and an upper bound of 1.16. For the mid term, the MBL was 1.2 ± 0.14 mm with a lower bound of 0.92 and an upper bound of 1.48. For the long term, the MBL change was 1.24 ± 0.16 mm with a lower bound of 0.92 and an upper bound of 1.56.
Conclusion: Based on this literature review, one-piece ceramic implants achieve osseointegration similar to titanium implants, with a stable MBL or a slight bone gain after an individual initial design depending on crestal remodeling. The risk of implant fracture is low for current commercially available implants. Immediate loading or temporization of the implants does not interfere with the course of osseointegration. Scientific evidence for two-piece implants is rare.
Schlagwörter: ceramic implants, implant survival, marginal bone level, systematic review, titanium implant
Implantologie, 4/2022
Seiten: 387-398, Sprache: DeutschHappe, Arndt / Debring, Leonie / Schmidt, Alexander / Fehmer, Vincent / Neugebauer, JörgEine randomisierte kontrollierte klinisch-volumetrische Studie Die Bindegewebetransplantation zählt heute zu den Standardverfahren zur Kompensation von Volumendefiziten bei Sofortimplantation. Neue Biomaterialien wie azelluläre Matrices könnten die Gewinnung autogenen Gewebes auf ein absolut notwendiges Minimum reduzieren und damit die Häufigkeit und das Ausmaß postoperativer Beschwerden verringern. Die vorliegende randomisierte Studie verglich die klinischen Therapieergebnisse von Sofortimplantationen in der Oberkieferfront, bei denen sowohl eine knöcherne Augmentation als auch eine Weichgewebeverdickung durchgeführt wurde. Neben anorganischem bovinem Knochenmaterial (ABBM) kam entweder ein Bindegewebeersatz aus porciner Dermis, eine azelluläre dermale Matrix (ADM) oder ein autogenes Bindegewebetransplantat (BGT) zum Einsatz. An der Studie nahmen 20 Patienten (11 Männer, 9 Frauen) mit einem Durchschnittsalter von 48,9 Jahren (21−72 Jahre) teil. Die Zuordnung der Studienteilnehmer zu der Test- (ADM) bzw. Kontrollgruppe (BGT) geschah nach dem Zufallsprinzip. Der Zahnextraktion folgte die sofortige Implantatinsertion. Der bukkale Knochen wurde mit ABBM augmentiert. Eine ADM oder ein BGT diente zur Verdickung des bukkalen Weichgewebes und somit zur Kompensation des erwarteten Verlustes von bukkalem Volumen. Die klinische und volumetrische Nachuntersuchung fand 12 Monate nach Implantatinsertion statt. Bei allen Implantaten hatte eine Osseointegration stattgefunden und die prothetische Versorgung befand sich in situ. Ein Jahr postoperativ betrug die durchschnittliche, linear gemessene Volumenveränderung −0,55 ± 0,32 mm (ADM) bzw. −0,60 ± 0,49 mm (BGT). Patienten der ADM-Gruppe beklagten signifikant weniger postoperative Beschwerden. Bei Sofortimplantation mit Augmentation von Hart- und Weichgewebe führten Ersatzmaterialien und autogene Bindegewebetransplantate zu ähnlichen klinischen Ergebnissen hinsichtlich der gemessenen Volumenveränderungen. Die Anwendung von Ersatzmaterial führte zu signifikant weniger postoperativer Morbidität.
Manuskripteingang: 07.01.2021, Annahme: 14.04.2021
Schlagwörter: Sofortimplantation, Weichgewebeverdickung, Bindegewebetransplantat, azelluläre dermale Matrix, anorganisches bovines Knochenmaterial
Implantologie, 3/2022
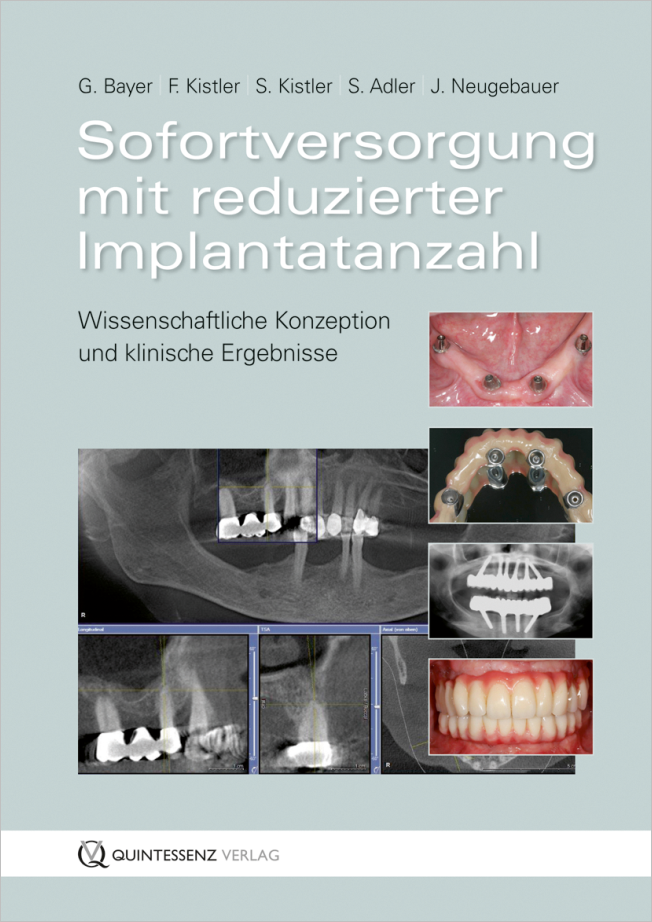
Seiten: 263-272, Sprache: DeutschKistler, Steffen / Kistler, Frank / Neugebauer, JörgFaktoren für den LangzeiterfolgDie Sofortimplantation mit Sofortversorgung in der ästhetischen Zone stellt eine Möglichkeit des langzeitstabilen Erhalts der periimplantären Weichgewebestrukturen dar. Neben der idealen Positionierung des Implantats ist die Gestaltung der provisorischen Versorgung essenziell für eine stabile Regeneration. Durch die Anwendung von Implantaten mit einem Plattform-Switch und einer bewussten Unterkonturierung kann sich ein Weichgewebesaum ausbilden, der über Jahre stabil bleibt und die Patientenerwartungen in der ästhetischen Zone erfüllt.
Manuskripteingang: 26.07.2022, Annahme: 03.08.2022
Schlagwörter: Sofortimplantation, Sofortversorgung, provisorische Versorgung, Plattform-Switch, Langzeitergebnis
International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 3/2022
DOI: 10.11607/prd.5632Seiten: 381-390, Sprache: EnglischHappe, Arndt / Debring, Leonie / Schmidt, Alexander / Fehmer, Vincent / Neugebauer, JörgConnective tissue grafts have become a standard for compensating horizontal volume loss in immediate implant placement. The use of new biomaterials like acellular matrices may avoid the need to harvest autogenous grafts, yielding less postoperative morbidity. This randomized comparative study evaluated the clinical outcomes following extraction and immediate implant placement in conjunction with anorganic bovine bone mineral (ABBM) and the use of a porcine acellular dermal matrix (ADM) vs an autogenous connective tissue graft (CTG) in the anterior maxilla. Twenty patients (11 men, 9 women) with a mean age of 48.9 years (range: 21 to 72 years) were included in the study and randomly assigned to either the test (ADM) or control (CTG) group. They underwent tooth extraction and immediate implant placement together with ABBM for socket grafting and either ADM or CTG for soft tissue augmentation. Twelve months after implant placement, the cases were evaluated clinically and volumetrically. All implants achieved osseointegration and were restored. The average horizontal change of the ridge dimension at 1 year postsurgery was -0.55 ± 0.32 mm for the ADM group and -0.60 ± 0.49 mm for the CTG group. Patients of the ADM group reported significantly less postoperative pain. Using xenografts for hard and soft tissue augmentation in conjunction with immediate implant placement showed no difference in the volume change in comparison to an autogenous soft tissue graft, and showed significantly less postoperative morbidity.
International Journal of Computerized Dentistry, 1/2022
SciencePubMed-ID: 35322651Seiten: 37-45, Sprache: Englisch, DeutschHappe, Arndt / von Glasser, Gerrit Schulze / Neugebauer, Jörg / Strick, Kilian / Smeets, Ralf / Rutkowski, RicoZiel: Evaluierung der Überlebensrate von implantatgetragenen Versorgungen, auf CAD/CAM-gefertigten Zirkoniumdioxid-Abutments mit einer Titanbasis.
Material und Methode: 153 Patienten mit insgesamt 310 Implantaten (Camlog Promote plus oder Xive S), die in den letzten 10 Jahren vollkeramische Versorgungen auf Abutments aus Yttrium-stabilisiertem Zirkoniumdioxid (3Y-TZP) mit Titanbasis erhielten, wurden eingeschlossen. Die Patienten wurden bei Routinebesuchen auf technische Komplikationen untersucht. Veränderungen des krestalen Knochenniveaus wurden anhand von periapikalen Röntgenaufnahmen von 75 Implantaten stichprobenartig analysiert.
Ergebnisse: Bei den 153 eingeschlossenen Patienten wurden 17 Keramikabplatzungen (5,5 %), 6 Abutmentlockerungen (1,9 %) und 2 Abutmentfrakturen (0,6 %) festgestellt. Die mittlere Nachbeobachtungszeit betrug 4,7 Jahre (Standardabweichung [SD]: 1,94), mit einer Nachbeobachtungszeit von bis zu 10 Jahren (Maximum). Die Kaplan-Meier-Analyse ergab eine Überlebensrate ohne Komplikationen von 91,6 % für die Restauration und 97,4 % für das Abutment. Es gab keinen statistisch signifikanten Unterschied bezüglich den beiden Implantatsystemen, der Implantatlokalisation oder der Komplikationsrate. Bei den 75 in die Röntgenanalyse einbezogenen Implantaten betrug die mittlere Knochenniveauveränderung 0,384 mm (SD: 0,242, 95% CI: 0,315 bis 0,452) für das Camlog Implantatsystem und 0,585 mm (SD: 0,366, 95% CI: 0,434 bis 0,736) für das Xive System (P = 0,007).
Schlussfolgerung: Die Ergebnisse dieser retrospektiven Studie zeigen akzeptable klinische Ergebnisse für Zirkonoxidabutments, die auf einer Titanbasis in Kombination mit Vollkeramikrestaurationen befestigt werden. Das untersuchte Abutment-Design scheint keine negativen Auswirkungen auf das periimplantäre Hartgewebe zu haben.
Schlagwörter: Implantat-Abutment, Zirkonoxid-Abutment, Titanbasis, zweiteiliges Abutment, Implantatversorgung